Risk Management



Management Structure of Risk Governance
Organization of the Risk Management Committee
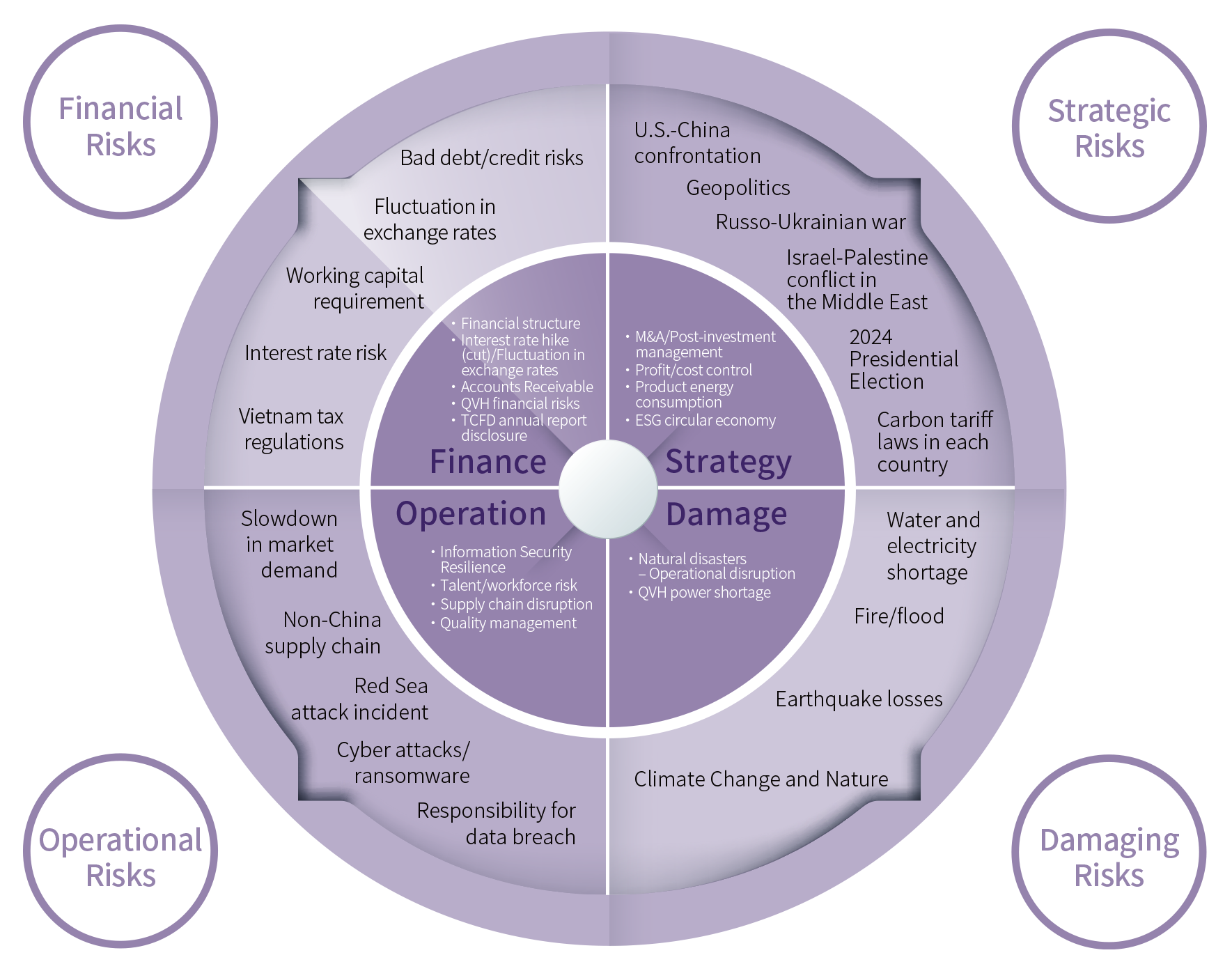
In June 2005, Qisda established the inter-departmental Risk Management Committee (RMC) to pursue the Company’ s goal of sustainable development and operation through consistent risk management based on four categories: strategy, finance, operation, and damage. With the President serving as the committee chair, the Sustainability & Risk Officer serving as the vice chairman, and the top-level executives of different units acting as the committee members, it discusses and determines the risk management strategies, decides on the risk appetite, and sets annual targets and risk performance indicators of Qisda.
A joint defense mechanism of over 180 companies, centering on Qisda, has been established to convene regular meetings, establish reporting channels, set up an information exchange platform, integrate group resources, and bring the unified strength into full play. To enhance the BOD's understanding and oversight capabilities regarding significant risk issues of the company, Qisda continuous provides annual training, seminar, instruction, or promotion on risk management topics to the directors, supported by diverse digital methods.
Qisda’s 2024 risk radar chart for risk identification
In addition, The Sustainability & Risk Officer is appointed to be the executive secretary of risk management to identify potential risks based on internal and external matters, prepare risk radar charts, arrange risk management meetings, conduct quarterly follow-ups to the risk targets, stay on top of the implementation of improvement plans, and facilitate interdepartmental communication. The operations of the Risk Management Committee are supervised by the Audit Committee/Board of Directors; a report on the implementation of risk management is submitted to the Audit Committee/Board of Directors every year.
Risk Management Process
The Risk Management Committee holds quarterly meetings and may convene special meetings for significant developments. The Chairman of the RMC outlines the major corporate-level risks for the year, and committee members identify and address risks within their respective units, developing risk mitigation strategies. We establish measurable Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) and track them quarterly to ensure our organizational objectives are met. During meetings, we review major domestic and international issues, regulatory changes, and unusual events, proposing effective response measures. Annually, we report the status of risk management operations to the Audit Committee and the Board of Directors
Business Continuity Management System (BCMS)
Qisda framed risk management policies and organized the Risk Management Committee (RMC) in 2005 in accordance with the ISO 31000 Risk Management–Principles and Guidelines.In 2024, Qisda’s Risk Management Committee identified a total of 37 key risks based on the risk radar chart and risk checklist. We formulate corresponding business continuity plans (BCPs) based on the simulation of various significant risk scenarios, and include these in the “Crisis Management Manual,” taking on a rolling-wave approach to management to lower impact and return to operations as fast as possible when facing risks. Additionally, the Group establishes a joint defense mechanism centered around Qisda, integrating the Group’s resources to strengthen our emergency response capabilities.
Qisda BCMs Framework
Risk Management Culture
A joint defense mechanism of over 180 companies, centering on Qisda, has been established to convene regular meetings, establish reporting channels, set up an information exchange platform, integrate group resources, and bring the unified strength into full play. To enhance the BOD's understanding and oversight capabilities regarding significant risk issues of the company, Qisda continuous provides annual training, seminar, instruction, or promotion on risk management topics to the directors, supported by diverse digital methods.
To foster a strong risk management culture, Qisda has integrated risk awareness into its performance management system and established a KPI framework based on this foundation to guide all employees toward unified goals. Various risk management indicators are incorporated into management performance evaluations, and Qisda’s three major risk control strategies are measured through KPIs, including:
(1) Revenue and profit are critical components of Qisda’s risk control strategy. Therefore, each department sets revenue and profit as KPI targets, accounting for 60% of the total performance evaluation, to ensure overall operational performance meets expectations.
(2) Key risk items are included in each unit’s KPIs. For example, to manage information security risks, the IT department sets a KPI to restore systems within six hours in the event of a disaster. The quality management team includes the validity of all certifications, while the manufacturing headquarters incorporates “zero fire incidents” and “zero occupational injuries” as KPI metrics.
(3) From the company level down to departments and individuals, team goals are further cascaded into individual performance targets, with risk identification and risk assessment included as recurring elements in each performance evaluation cycle.




Want to know more detailed content?
Read Report Contents